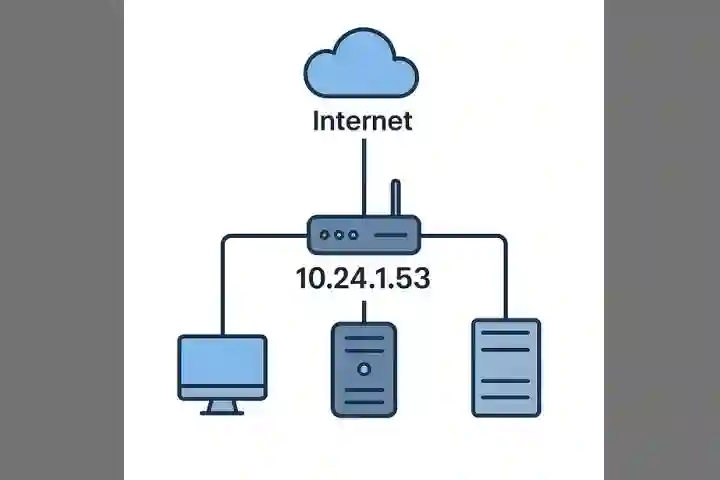
The IP address 10.24.1.53 is a private IPv4 address that falls within the 10.0.0.0/8 range reserved for internal network use under RFC 1918. It is typically assigned to devices or servers operating within a secure local area network (LAN) or a virtual private network (VPN). Such addresses are not publicly routable, meaning they require Network Address Translation (NAT) for external communication, enhancing both security and control within organizational infrastructures.
In most environments, 10.24.1.53 could belong to a server, workstation, or network appliance hosting internal applications or services. It often uses static configuration for reliability, supported by internal DNS resolution and monitoring tools. Proper configuration, patching, and restricted access help maintain the stability and security of systems using this address.
Table of Contents
Introduction to 10.24.1.53
The IP address 10.24.1.53 is a private IPv4 address commonly used in local area networks (LANs). It belongs to the reserved range of IP addresses designated for private use, meaning it cannot be accessed directly from the public internet. Instead, it functions as an identifier for a specific device — such as a computer, router, or printer — within an internal network.
Private IP addresses like 10.24.1.53 are essential in modern networking because they allow devices to communicate within a closed system without requiring a unique public IP for each device. This not only conserves IP resources but also enhances security by isolating internal traffic from the outside world.
Technical Context and Use
In practical networking environments, 10.24.1.53 might be assigned dynamically by a DHCP server or configured manually by an IT administrator. You might encounter this IP when managing routers, accessing internal dashboards, or troubleshooting network devices. It’s particularly common in enterprise infrastructures, educational institutions, and private labs that use structured subnetting for efficient network segmentation.
Understanding the Concept of Private IP Addresses
What Is a Private IP Address?
A private IP address is an IP reserved for internal network communication. According to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), private IPs are not routable on the global internet. They are used within homes, offices, and corporate networks to facilitate data exchange between devices without requiring external connectivity.
Private IPs reduce the demand for public IPs and enhance internal data privacy. They allow devices like printers, servers, IoT appliances, and desktops to interact locally while using Network Address Translation (NAT) to connect externally through a shared public IP when needed.
Private vs Public IP Addresses
The major difference between private and public IPs lies in accessibility and visibility.
- Private IPs (like 10.24.1.53) exist only within local networks and cannot be accessed from the internet.
- Public IPs are assigned by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and are globally unique, allowing worldwide communication.
For instance, if your router has a public IP, it connects to the internet on your behalf. The devices inside your home — each with private IPs — communicate through that router via NAT.
The 10.x.x.x Range
The 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 range is one of three major private IPv4 blocks defined by RFC 1918. This specific range is extremely flexible, supporting over 16 million IP addresses — ideal for large networks and corporations.
Other private ranges include:
- 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
Within this structure, 10.24.1.53 sits neatly as part of the 10.x.x.x block, likely within a smaller subnet defined for specific departments or zones in a network.
Technical Details of 10.24.1.53
IP Classification and Range
The IP 10.24.1.53 falls under Class A of the IPv4 addressing system. Class A addresses start with values from 1.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255 and are typically used for very large networks.
Being in this range, 10.24.1.53 provides a broad host capacity — suitable for enterprise-scale setups where thousands of devices might share the same network space.
Subnet and Mask Information
Typical subnet configurations for 10.24.1.53 include 255.0.0.0 (default Class A mask) or smaller subnets like 255.255.255.0 for departmental segmentation. These subnet masks help divide large networks into smaller, manageable portions while maintaining performance and security.
Associated Devices and Servers
10.24.1.53 could belong to various internal devices, including:
- Network routers or gateways
- File or print servers
- CCTV or IoT controllers
- Workstations in an enterprise network
- Development or testing servers
Such assignments are controlled via DHCP or manually defined static configurations.
Common Uses of 10.24.1.53
Local Network Configuration
In local environments, administrators assign IPs like 10.24.1.53 to specific devices to ensure consistent communication. It might serve as a node within a subnet reserved for operations, logistics, or testing.
Router Login and Admin Panels
Occasionally, internal routers or switches use addresses such as 10.24.1.53 for web-based login panels. By typing this IP into a browser, admins can access configuration settings, monitor network health, and manage connected devices.
Internal Web Applications
In corporate networks, web applications and dashboards are often hosted on private IPs. 10.24.1.53 may lead to an intranet page, inventory system, or internal analytics portal that’s only available to authorized staff.
How to Access 10.24.1.53 Safely
Using the Web Browser Method
To check if 10.24.1.53 hosts a web-based admin interface:
- Connect your device to the same local network.
- Open a web browser.
- Enter http://10.24.1.53 in the address bar.
If configured, you’ll reach a login portal; otherwise, the request will time out.
Command Line and Network Tools
You can test connectivity using tools like:
- ping 10.24.1.53 – Checks if the device is active.
- ipconfig /all (Windows) or ifconfig (Linux/Mac) – Displays your local network details.
- tracert 10.24.1.53 – Shows routing paths within your LAN.
Troubleshooting Access Issues
If 10.24.1.53 isn’t reachable:
- Ensure your device is on the same subnet.
- Disable any VPNs or proxies that might interfere.
- Restart your router or check for IP conflicts.
- Clear browser cache or try another device.
Security Aspects of 10.24.1.53
Network Security Risks
Even though private IPs are not exposed to the internet, internal breaches can occur if devices are misconfigured. Attackers within the network could exploit weak admin passwords or unpatched firmware.
Importance of Firewalls and Access Control
Firewalls play a crucial role in securing private IPs like 10.24.1.53. They filter internal and outbound traffic, ensuring only authorized users can interact with sensitive devices. Implementing MAC filtering, role-based access, and strong encryption further minimizes risk.
Safe Practices for IT Administrators
- Use complex passwords for internal web panels.
- Regularly update firmware and software.
- Restrict IP access using VLAN segmentation.
- Perform periodic vulnerability scans.
Troubleshooting and Configuration
Identifying Network Conflicts
When two devices share the same IP (like 10.24.1.53), both will experience connectivity issues. Tools like arp -a or router logs help identify conflicting MAC addresses.
Resetting or Changing IP Assignments
If conflicts persist, change the IP manually:
- On Windows: Go to Network & Internet Settings → Change Adapter Options → IPv4 Settings.
- On Routers: Access the DHCP table and reassign IPs dynamically.
Checking Device Logs and Network Settings
System logs can reveal which device holds the IP 10.24.1.53 and its recent activity. Routers often display this under “Connected Devices” or “DHCP Lease Table.”
Applications and Use Cases
Educational or Testing Environments
In universities and IT training labs, private IPs like 10.24.1.53 are used to simulate real-world networking setups. They allow students to practice without exposing devices to the public web.
Corporate IT Infrastructure
Enterprises rely heavily on private IP ranges for internal communications, remote management, and server hosting. Addresses like 10.24.1.53 often belong to monitoring servers or database backends that support internal applications.
Smart Home and IoT Networks
IoT devices — such as cameras, thermostats, and lighting systems — often use private IPs for communication. 10.24.1.53 might represent one such device within a local smart ecosystem.
Challenges Related to 10.24.1.53
Limited External Accessibility
Since 10.24.1.53 is not routable on the public internet, users outside the network cannot reach it. This limits remote access unless configured via VPN or port forwarding.
Misconfiguration Issues
Errors in subnetting or DHCP assignment can disrupt communication. For example, if your gateway and device are in different subnets, connectivity fails even if the IP exists.
Network Overlaps in Large Organizations
When multiple branches use the same private IP ranges, overlap can occur. Network engineers must carefully design subnets to avoid such conflicts.
Best Practices for Managing 10.24.1.53
Regular Network Monitoring
Use tools like Wireshark, PRTG, or Nagios to monitor data flow, detect anomalies, and ensure that 10.24.1.53 remains secure and operational.
Documenting IP Assignments
Keeping an updated IP address management (IPAM) record prevents duplication and simplifies troubleshooting. Each device’s IP, MAC, and purpose should be logged systematically.
Updating Security and Firmware
Outdated firmware can create vulnerabilities. Always schedule routine updates and enable automatic patching where possible to ensure optimal network protection.
Future of Private IP Networking
IPv6 and the Evolution of Local Networks
IPv6 introduces an almost unlimited address space, reducing dependency on private IPv4 addresses like 10.24.1.53. However, IPv4 remains dominant in many existing infrastructures.
Automation and Smart Network Management
Modern networks increasingly use AI-based IP management tools that detect conflicts, predict usage patterns, and automatically optimize resource allocation.
Integration with Cloud and Hybrid Systems
Private IPs now extend into hybrid environments, linking on-premises infrastructure with cloud systems through VPNs and secure tunnels — ensuring seamless, secure communication.
Conclusion
The IP 10.24.1.53 is a private IPv4 address within the 10.0.0.0/8 range, primarily used in internal networks for communication, testing, and management. It ensures local connectivity while remaining isolated from the public internet, enhancing both performance and security.
Understanding how private IPs like 10.24.1.53 function is essential for IT professionals, students, and home users. Proper configuration, security measures, and documentation transform such IPs into reliable building blocks of modern digital infrastructure.
FAQs about 10.24.1.53
What is 10.24.1.53 used for?
It’s a private IP address used within local networks for internal communication or device configuration.
Is 10.24.1.53 a public or private IP address?
It’s a private IP, reserved for internal use as defined by IANA.
How can I log in to 10.24.1.53?
You can access it through a web browser (if it hosts an admin interface) or via network tools like ping or SSH (if enabled).
Why can’t I access 10.24.1.53 from the internet?
Because private IPs are not routable over the public web — they’re designed for internal LAN environments only.
What devices typically use this IP address?
It could be assigned to routers, internal servers, IoT devices, or computers within an organization’s private network.
Also read : HRMS Delhivery